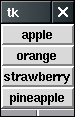
Ruby/Tkでは各種ウィジェットクラスのメソッドとしてpackを呼び出します.
#!/usr/local/bin/ruby
require 'tk'
w1 = TkLabel.new(nil, 'text' => 'apple', 'relief' => 'raised')
w1.pack('side' => 'top', 'fill' => 'both')
w2 = TkLabel.new(nil, 'text' => 'orange', 'relief' => 'raised')
w2.pack('side' => 'top', 'fill' => 'both')
w3 = TkLabel.new(nil, 'text' => 'strawberry', 'relief' => 'raised')
w3.pack('side' => 'top', 'fill' => 'both')
w4 = TkLabel.new(nil, 'text' => 'pineapple', 'relief' => 'raised')
w4.pack('side' => 'top', 'fill' => 'both')
Tk.mainloop
上記のプログラムを走らせると,下のようになります.

packメソッドの書式は,
pack(['arg_key1' => value1, 'arg_key2' => value2, ...])
です. packメソッドは0個以上の引数を持ちます.引数は全てハッシュの形式で記述します.
| キーの名前 | 働き |
|---|---|
| side | 'top','bottom','left'または'right'のいづれかの値をもつ.未配置領域の中から,割り当てる領域を決定する. |
| fill | 割り当てられた領域を広げる.'none','x','y','both'で指定する. |
| padx,pady | ウィジェットの外側に追加する余白の量.整数値で指定する. |
| ipadx,ipady | ウィジェットの内側に追加する余白の量.整数値で指定する. |
| expand | 領域の余白を割り当てるか.論理値(1や'no'の値)で指定する. |
| anchor | 割り当てられた領域のどこに配置するか指定.'c','n','ne','e','se','s','sw','w'','nw'で指定. |
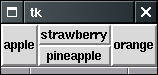
packはsideと順番が大事です.sideを変えるとレイアウトもかわります.
#!/usr/local/bin/ruby
require 'tk'
w1 = TkLabel.new(nil, 'text' => 'apple', 'relief' => 'raised')
w1.pack('side' => 'left','fill' => 'both')
w2 = TkLabel.new(nil, 'text' => 'orange', 'relief' => 'raised')
w2.pack('side' => 'right', 'fill' => 'both')
w3 = TkLabel.new(nil, 'text' => 'strawberry', 'relief' => 'raised')
w3.pack('side' => 'top', 'fill' => 'both')
w4 = TkLabel.new(nil, 'text' => 'pineapple', 'relief' => 'raised')
w4.pack('side' => 'bottom', 'fill' => 'both')
Tk.mainloop
上のプログラムの場合,以下のようになります.